language
English
العربية
বাংলাদেশ
Български
Hrvatski
Česky
Dansk
Nederland
 Esperanto
Esperanto
Slovenski
Filipino
Suomi
Français
Maori
 Shqiptare
Shqiptare
Georgian
 Euskara
Euskara
Deutsch
Ελλάδα
ישראל
इंडिया
Magyarország
Ísland
Indonesia
Irlanda
Italia
日本語
Sovensko
Հայաստան
한국
Kyrgyz
ປະເທດລາວ
 Zulu
Zulu
Latvian
Lithuanian
Luxembourgish
 Latinus
Latinus
Macedonian
Малайская
Maltese
Монгол улс
 Cymraeg
Cymraeg
ဗမာ
 தமிழ்
தமிழ்
नेपाल
Norge
ایران
Polska
Portugal
România
Российская
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Србија
 Slovak
Slovak
Bosanski
Slovenian
Беларус
España
Sverige
Точик
ประเทศไทย
Türk
Azərbaycan
Uzbek
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Việt Nam
Unveiling the Secrets of High-Frequency Test Probes: A Comprehensive Guide
Source:
Author:
Unveiling the Secrets of High-Frequency Test Probes: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to High-Frequency Test Probes
- 2. Understanding High-Frequency Test Probes
- 3. Applications of High-Frequency Test Probes
- 3.1 High-Frequency Test Probes in Electronics
- 3.2 Industrial Applications of High-Frequency Test Probes
- 4. Types of High-Frequency Test Probes
- 5. Choosing the Right High-Frequency Test Probe
- 6. Best Practices for Using High-Frequency Test Probes
- 7. Frequently Asked Questions About High-Frequency Test Probes
- 8. Conclusion
1. Introduction to High-Frequency Test Probes
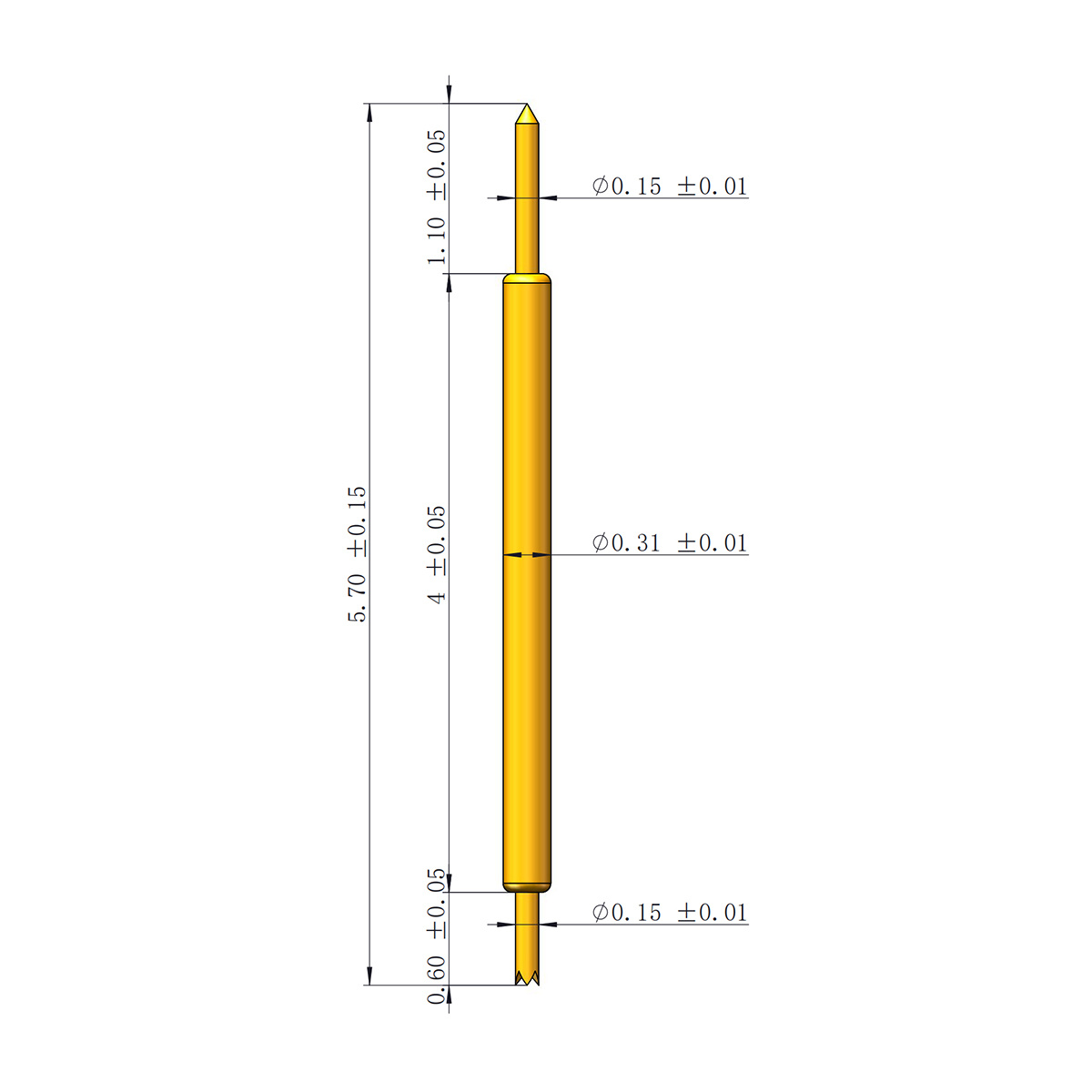
High-frequency test probes are essential tools in the realm of electronics and electrical engineering. They serve as the link between the measuring instrument and the circuit under observation, allowing for accurate readings in high-frequency environments. These specialized probes are crucial for ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices, especially in today’s fast-paced technological landscape.
2. Understanding High-Frequency Test Probes
2.1 What Are High-Frequency Test Probes?
High-frequency test probes are devices designed to measure electrical signals in circuits where frequencies exceed 1 MHz. They are engineered to minimize the effects of stray capacitance and inductance, providing precise measurements while effectively isolating the probing system from the circuit.
2.2 How Do High-Frequency Test Probes Work?
These probes operate by converting electrical signals into measurable data with minimal interference. They consist of a conductive tip that contacts the circuit and a cable that carries the signal to an oscilloscope or other measuring device. The design of high-frequency probes helps maintain the integrity of the signal, ensuring accurate readings.
3. Applications of High-Frequency Test Probes
3.1 High-Frequency Test Probes in Electronics
In the electronics industry, high-frequency test probes are used extensively for signal integrity testing, debugging, and performance evaluation of high-speed digital circuits. They play a vital role in the design and testing of printed circuit boards (PCBs), particularly in applications involving RF (radio frequency) signals.
3.2 Industrial Applications of High-Frequency Test Probes
Beyond consumer electronics, high-frequency test probes are indispensable in industrial automation, telecommunications, and aerospace applications. They ensure that systems perform as expected, enhancing safety and functionality in critical environments.
4. Types of High-Frequency Test Probes
4.1 Passive Probes
Passive probes are the most common type of high-frequency test probes. They do not require external power and are straightforward to use. However, they have limitations in terms of bandwidth and signal integrity, making them more suitable for low to moderate frequency applications.
4.2 Active Probes
Active probes incorporate an internal amplifier, allowing them to offer better bandwidth and lower loading effects. These probes require external power but provide superior performance, making them ideal for high-frequency measurements.
4.3 Differential Probes
Differential probes are designed to measure the voltage difference between two points in a circuit without referencing ground. This capability is invaluable for avoiding ground loops and ensuring accurate measurements in high-speed differential signaling applications.
5. Choosing the Right High-Frequency Test Probe
Selecting the appropriate high-frequency test probe involves considering factors such as bandwidth, input impedance, and the specific characteristics of the circuit being tested. Understanding the nuances of different probes is crucial for achieving optimal results in measurements.
6. Best Practices for Using High-Frequency Test Probes
To maximize the effectiveness of high-frequency test probes, follow these best practices:
1. **Minimize Probe Loading**: Choose probes with high input impedance to reduce the impact on the circuit.
2. **Use Short Cables**: Keep cable lengths short to reduce inductance and capacitance.
3. **Calibrate Regularly**: Regular calibration of probes ensures accurate measurements.
4. **Proper Grounding**: Ensure that the probe is properly grounded to prevent noise interference.
5. **Maintain Clean Connections**: Regularly clean probe tips to maintain contact quality.
7. Frequently Asked Questions About High-Frequency Test Probes
1. What is the frequency range of high-frequency test probes?
High-frequency test probes typically operate in the range of 1 MHz to several GHz, depending on the specifications of the probe.
2. How do I know which probe to use for my application?
Consider the frequency range, input impedance, and the specific requirements of your application when selecting a probe.
3. Are active probes worth the investment?
Yes, active probes offer better bandwidth and signal integrity, making them suitable for high-frequency applications where precision is crucial.
4. Can I use passive probes for high-frequency measurements?
While passive probes can be used for high-frequency measurements, they may not provide the same level of accuracy and performance as active probes.
5. How should I store my high-frequency test probes?
Store probes in a protective case or holder to prevent damage and ensure longevity. Additionally, keep them in a clean and dry environment to avoid corrosion.
8. Conclusion
High-frequency test probes are pivotal in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of electronic devices in a world increasingly reliant on high-speed technology. By understanding their types, applications, and best practices, professionals can enhance their measurement capabilities and contribute to the successful development of advanced electronic systems. Embracing the intricacies of high-frequency test probes will not only improve testing precision but will also foster innovation in the ever-evolving landscape of electronics.
在线客服
Lanyi Electronics - Semiconductor Test Probe Manufacturing Plant
Customer first, quality first, unity and cooperation, mutual benefit and win-win

Copyright © 2022 Dongguan Lanyi Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. 粤ICP备17061266号 Powered by www.300.cn SEO